
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2 Department of Physics, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
![]()
![]() All-inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots (QDs) have received great attention in white light emission because of their outstanding properties. However, their practical application is hindered by poor stability. Herein, we propose a simple strategy to synthesize excellent stability and efficient emission of CsPbBr3 QDs by using 2-hexyldecanoic acid (DA) as a ligand to replace the regular oleic acid (OA) ligand. Thanks to the strong binding energy between DA ligand and QDs, the modified QDs not only show a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) of 96% but also exhibit high stability against ethanol and water. Thereby warm white light-emitting diodes (WLEDs) are constructed by combining ligand modified CsPbBr3 QDs with red AgInZnS QDs on blue emitting InGaN chips, exhibiting a color rendering index of 93, a power efficiency of 64.8 lm/W, a CIE coordinate of (0.44, 0.42) and correlated color temperature value of 3018 K. In addition, WLEDs based on ligand modified CsPbBr3 QDs also exhibit better thermal performance than that of WLEDs based on the regular CsPbBr3 QDs. The combination of improved efficiency and better thermal stability with high color quality indicates that the modified CsPbBr3 QDs are ideal for WLEDs application.
All-inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots (QDs) have received great attention in white light emission because of their outstanding properties. However, their practical application is hindered by poor stability. Herein, we propose a simple strategy to synthesize excellent stability and efficient emission of CsPbBr3 QDs by using 2-hexyldecanoic acid (DA) as a ligand to replace the regular oleic acid (OA) ligand. Thanks to the strong binding energy between DA ligand and QDs, the modified QDs not only show a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) of 96% but also exhibit high stability against ethanol and water. Thereby warm white light-emitting diodes (WLEDs) are constructed by combining ligand modified CsPbBr3 QDs with red AgInZnS QDs on blue emitting InGaN chips, exhibiting a color rendering index of 93, a power efficiency of 64.8 lm/W, a CIE coordinate of (0.44, 0.42) and correlated color temperature value of 3018 K. In addition, WLEDs based on ligand modified CsPbBr3 QDs also exhibit better thermal performance than that of WLEDs based on the regular CsPbBr3 QDs. The combination of improved efficiency and better thermal stability with high color quality indicates that the modified CsPbBr3 QDs are ideal for WLEDs application.
CsPbBr3 quantum dots ligand modification stability efficiency white light-emitting diodes Opto-Electronic Advances
2022, 5(1): 200075

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
Inorganic halide perovskites (IHPs) have received substantial attention due to their unique optoelectronic properties. Among all the intriguing performance, the efficient luminescence of IHPs enables the practical application of white light-emitting diodes (WLEDs) for lighting. During the last decade, IHP-based white lighting sources with a high luminesce and a broad color gamut have been developed as strong competitors to conventional and classic WLEDs based on rare-earth phosphors and blue LED chips. Thus, it inspires us to give an overview of the emerging progress of IHP WLEDs that can function as lighting sources. Here, in this review, the generation of luminescent properties and white light in IHPs are first presented. Then, both photoluminescence and electroluminescence WLEDs with IHPs emitters, including both lead-based and lead-free IHPs, are synthetically discussed to exhibit their advantages. Furthermore, the efforts on the optical performance enhancement of IHPs in WLEDs are demonstrated and summarized. Apart from WLEDs, visible light communication based on IHPs featuring efficient luminescence is proposed to highlight their promising potential in lighting communication. Finally, some perspectives on the evolution and challenges are described, followed by an inspirational outlook on their future development.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(4): 04001039

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & System (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
Solution-processed oxide semiconductors have been considered as a potential alternative to vacuum-based ones in printable electronics. However, despite spin-coated InZnO (IZO) thin-film transistors (TFTs) have shown a relatively high mobility, the lack of carrier suppressor and the high sensitivity to oxygen and water molecules in ambient air make them potentially suffer issues of poor stability. In this work, Al is used as the third cation doping element to study the effects on the electrical, optoelectronic, and physical properties of IZO TFTs. A hydrophobic self-assembled monolayer called octadecyltrimethoxysilane is introduced as the surface passivation layer, aiming to reduce the effects from air and understand the importance of top surface conditions in solution-processed, ultra-thin oxide TFTs. Owing to the reduced trap states within the film and at the top surface enabled by the doping and passivation, the optimized TFTs show an increased current on/off ratio, a reduced drain current hysteresis, and a significantly enhanced bias stress stability, compared with the untreated ones. By combining with high-capacitance AlOx, TFTs with a low operating voltage of 1.5 V, a current on/off ratio of > 10 4 and a mobility of 4.6 cm2/(V·s) are demonstrated, suggesting the promising features for future low-cost, low-power electronics.
Journal of Semiconductors
2022, 43(3): 034102
在现代社会中,白光发光二极管(LED)在照明和显示背板等诸多领域都有着重要的基础性作用。为了获得具有优异性能的白光LED,首先需要获得满足白光LED发光需要的高性能的发光材料。而作为一类新兴的半导体材料,无机钙钛矿(CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, I)由于其具有的高发光量子产率、发光波长可调、色纯度高和稳定性好等优点,在发光应用特别是白光LED领域展现出了巨大的潜力。文中将首先分别从光致白光LED和电致白光LED两个方面出发,综述近期在基于无机钙钛矿的白光LED方面所取得的研究进展,随后分别介绍以上两个体系中改性后的无机钙钛矿发光材料与其他发光材料复合形成白光以及无机钙钛矿单组分白光的代表性成果。最后,对钙钛矿白光LED在可见光通信方面所取得的最新进展进行介绍,并且对白光LED以及可见光通信的研究发展趋势与挑战进行了总结和展望。
白光LED 钙钛矿发光材料 可见光通信 white LEDs perovskites luminescent material visible light communication 红外与激光工程
2022, 51(1): 20210772

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
Inorganic cesium lead halide (, , Br, I) nanocrystals (NCs) attract extensive attention because of their excellent optoelectronic performance. However, the classic NCs suffer from toxicity and instability, which impede their further applications in commercial fields. Here the inorganic lead-free cesium copper chlorine NCs are synthesized by a facile hot-injection method. The blue-emission 3D and green-emission 0D NCs are prepared at 70°C and 120°C, respectively, suggesting that the reaction temperature may account for the final components. Owing to the self-trapped exciton effect, the unique optical properties, such as high photoluminescence (PL) quantum yield, broadband emission, large Stokes shift, and long PL decay time, are demonstrated for both cesium copper chlorine NCs. Moreover, highly efficient and stable warm white light-emitting diodes are fabricated with and NCs. The study highlights the promising potential for lead-free cesium copper chlorine nanocrystals in nontoxic solid-state lighting applications.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(2): 02000187
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
4 e-mail: dujuan@mail.siom.ac.cn
5 e-mail: zangzg@cqu.edu.cn
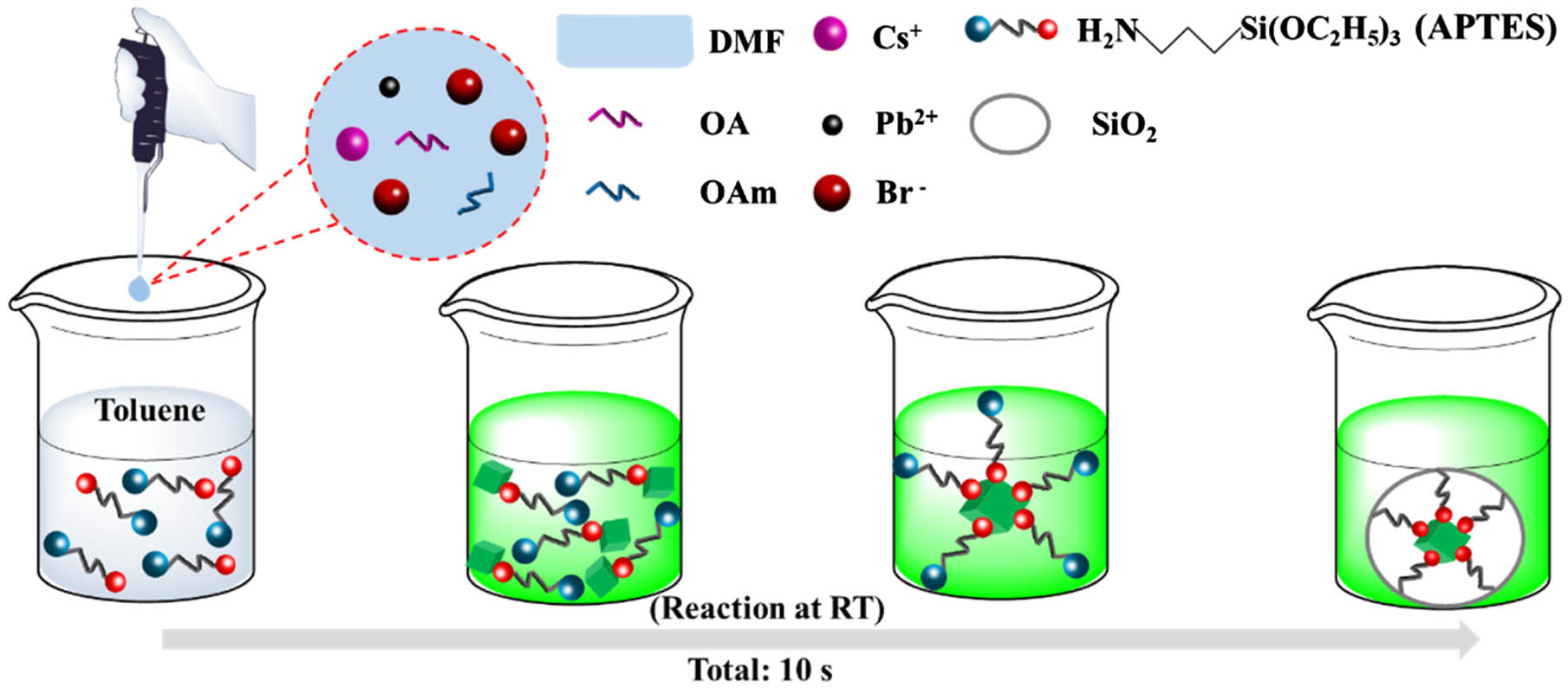
All-inorganic cesium lead bromide () perovskite quantum dots (QDs) with excellent optical properties have been regarded as good gain materials for amplified spontaneous emission (ASE). However, the poor stability as the results of the high sensitivity to heat and moisture limits their further applications. Here, we report a facile one-pot approach to synthesize QDs at room temperature. Due to the effective defects passivation using , as-prepared QDs present an enhanced photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) and chemical stability. The PLQY of QDs reaches 71.6% which is higher than 46% in pure QDs. The PL intensity of QDs maintains 84% while remaining 24% in pure after 80 min heating at 60°C. The ASE performance of the films is also studied under a two-photon-pumped laser. Compared with the films using pure QDs, those with as-prepared QDs exhibit a reduced threshold of ASE. The work suggests that room-temperature-synthesized -coated perovskites QDs are promising candidates for laser devices.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(10): 10001605

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
All inorganic perovskite quantum dots (QDs) have been recognized as promising optical materials to fabricate green light emission devices because of their excellent optical performance. However, regular QDs with an oleic acid (OA) ligand show poor stability, which limits their practical application. We replaced the OA ligand in QDs with a 2-hexyldecanoic acid (DA) ligand and, in the synthesis, found that the new material has better optical properties than regular QDs ( QDs). Due to the strong binding energy between the DA ligand and QDs, the ligand-modified QDs ( QDs) show a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) of 96%, while the PLQY of QDs is 84%. Subsequently, the QDs coated on the blue light-emitting diode (LED) chips as green phosphors are demonstrated. The color conversion from blue to pure green is achieved by adding the QDs solution up to 60 μL, while the pure green emission devices only need 18 μL QDs solution under the same concentration. The ultrapure, highly efficient green light-emitting devices based on QDs exhibit a luminous efficiency of 43.6 lm/W with a CIE (0.2086, 0.7635) under a 15.3 mA driving current. In addition, the green emission wavelength of the devices based on QDs almost has no shift, even under a high injection current. These results highlight the promise of DA ligand-modified QDs for light-emitting devices and enrich the application field of ligand-modified QDs.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(7): 07001086

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology & Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2 Key Laboratory of Low-Grade Energy Utilization Technologies and Systems (Ministry of Education), Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
Unlike organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites, all-inorganic cesium lead halide perovskites hold great promise for developing high-performance optoelectronic devices, owing to their improved stability. Herein, we investigate the perovskite-related CsPb2Br5 nanoplatelets (NPLs) with tunable emission wavelengths via changing the reaction temperatures to 100°C, 120°C, and 140°C. Reaction temperature plays a key role in determining the shapes and thicknesses of the resulting CsPb2Br5 NPLs. A higher temperature is in favor of the formation of smaller and thicker NPLs. To develop their potential applications in optoelectronic devices, green light emitting diodes (LEDs) and photodetectors based on CsPb2Br5 NPLs are fabricated. The green LEDs based on CsPb2Br5 NPLs synthesized at 140°C exhibit an excellent pure green emission (full width at half-maximum of <20 nm) and display a luminous efficiency of 34.49 lm/W under an operation current of 10 mA. Moreover, the photodetector based on CsPb2Br5 NPLs synthesized at 100°C has better performance with a rise time of 0.426 s, a decay time of 0.422 s, and a ratio of the current (with and without irradiation) of 364%.
(160.4236) Nanomaterials (160.4670) Optical materials (230.3670) Light-emitting diodes (040.5160) Photodetectors. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000473